The end seminar of ForestPotential was held at Bikuben, NMBU on the 24th of November 2022.
Kategoriarkiv: ForestPotential
Ny feltkampanje for overvåking av den alpine tregrensen i Norge gjennomført sommeren 2022
Feltarbeid 2020
I løpet av august og september 2020, ble det gjort en enorm innsats for å samle jordprøver i den alpine tregrensen.
Prosjektmøte
Den 10 mars, 2020 var de nasjonale prosjektpartnerne i ForestPotential samlet til møte
Feltarbeid 2018
Masteroppgave: Allelopatisk effekt av krekling på rekruttering og overlevelse av pionertrær i tregrenseøkotonen.
Oppstartsmøte
Oppstartsmøtet for ForestPotential var en suksess

Fra venstre: Geir Korsvold, Lennart Noordermeer, Gunnar Austrheim, Nicholas Coops, James Speed, Kari Klanderud, Vegard Lien, Hans Fredrik Hoen, Ole Martin Bollandsås, Karen Lone, Asbjørn Aaheim
ForestPotential hadde oppstartsmøte på RunWay konferansehotell på Gardermoen 22 og 23 mars 2018. De fleste partnerne var tilstede eller deltok via nettet.
På møtet introduserte partnerne sitt ekspertiseområde og nylige forskningsaktiviteter relevante for prosjektet. Hver arbeidspakke ble deretter presentert og diskutert i detalj. Diskusjonene var veldig nyttige og utsiktene til et givende samarbeid og at prosjektet vil nå sine mål, ser lovende ut.
Masteroppgave: Regionale forskjeller i rekruttering, mortalitet og vekst for pionertrær i tregrenseøkotonen
Det er mange faktorer som påvirker dynamikken i tregrenseøkotonen. Både klima, beiting og endret arealbruk er bestemmende for både rekruttering, mortalitet og vekst i denne overgangssonen mellom skog og fjell. I tillegg til at det kan være vanskelig å kvantifisere effekten av den enkelte faktor, finnes det også svært mange lokale faktorer som er med på bestemme endringene slik som bunnvegetasjonsforhold, mikrotopografi, hellingsretning etc. Denne masteroppgaven vil ved hjelp av multi-temporale observasjoner av trær i tregrenseøkotonen på 35 lokaliteter langs en over 1000 km lang breddegradsgradient, undersøke i hvilken grad det er regionale forskjeller med tanke på endringer i rekruttering, mortalitet og vekst for disse trærne. Oppgaven vil også undersøke i hvilken grad endingene kan forklares med klimadata og data for beitende husdyr og vilt rundt de ulike lokalitetene. Oppgaven er knyttet til prosjektet ForestPotential.
Masterstudent: Kenneth Langlie Simensen.
Veiledere: Ole Martin Bollandsås, Kari Klanderud
ForestPotential
«Changing Forest Area and Forest Productivity – Climatic and Human Causes, Effects, Monitoring Options, and Climate Mitigation Potential»
Project summary
A changing climate affects both the growth and the potential extent of our forests. Quantification of the effects is, however, not a trivial task. Climate change involves both changes in temperature and precipitation and studies have predicted that the magnitude of these changes will vary across latitudinal and altitudinal gradients. The competitive relationships between different vegetation species are also likely to change with changes in climate. In the boreal-alpine and boreal-tundra tree line ecotones, the changes are expected to be most rapid, both because trees here to a large degree grow on their tolerance limit in terms of climatic conditions, but also because the number of grazing domestic animals have declined in the last decades. A potential increased forest area because of upwards- and northwards shifts in the tree line will have an effect on carbon sequestration, but also the albedo effect and biodiversity in the tree line ecotone. Even for the forests well below the tree line, the growth conditions will change with changes in climate. Increased productivity will have impact both on the climate mitigation potential of the forest sector as well as the sector’s economic potential.
By means of time series data of the growth of trees, both on the productive forest land and in the tree line ecotone, coupled with time series data of climate, herbivory, airborne laser scanning, imagery, and multi-spectral information, the project ForestPotential aims at answering the several important research questions. What are the relative importance of grazing and climate on recruitment and growth in the tree line ecotone, and how accurately can changes be monitored using remotely sensed data? Can bi-temporal airborne laser scanner data be used to accurately estimate forest productivity? With input from the analyses of these research questions, we will also carry out long-term, large-scale forecasts of the Norwegian forest sector, also accounting for the albedo effect and the dynamics of the forest soil carbon stocks.
Dataset
Rollag: Within a 200 x 600 m area, over a ridge in Rollag municipality, detailed measurements of trees in the tree line ecotone have been carried out. The development of these trees have been followed over a period of 12 years (2006-2018). The datast will primarely be used for development of a system for monitoring the tree line ecotone using remote sensing.
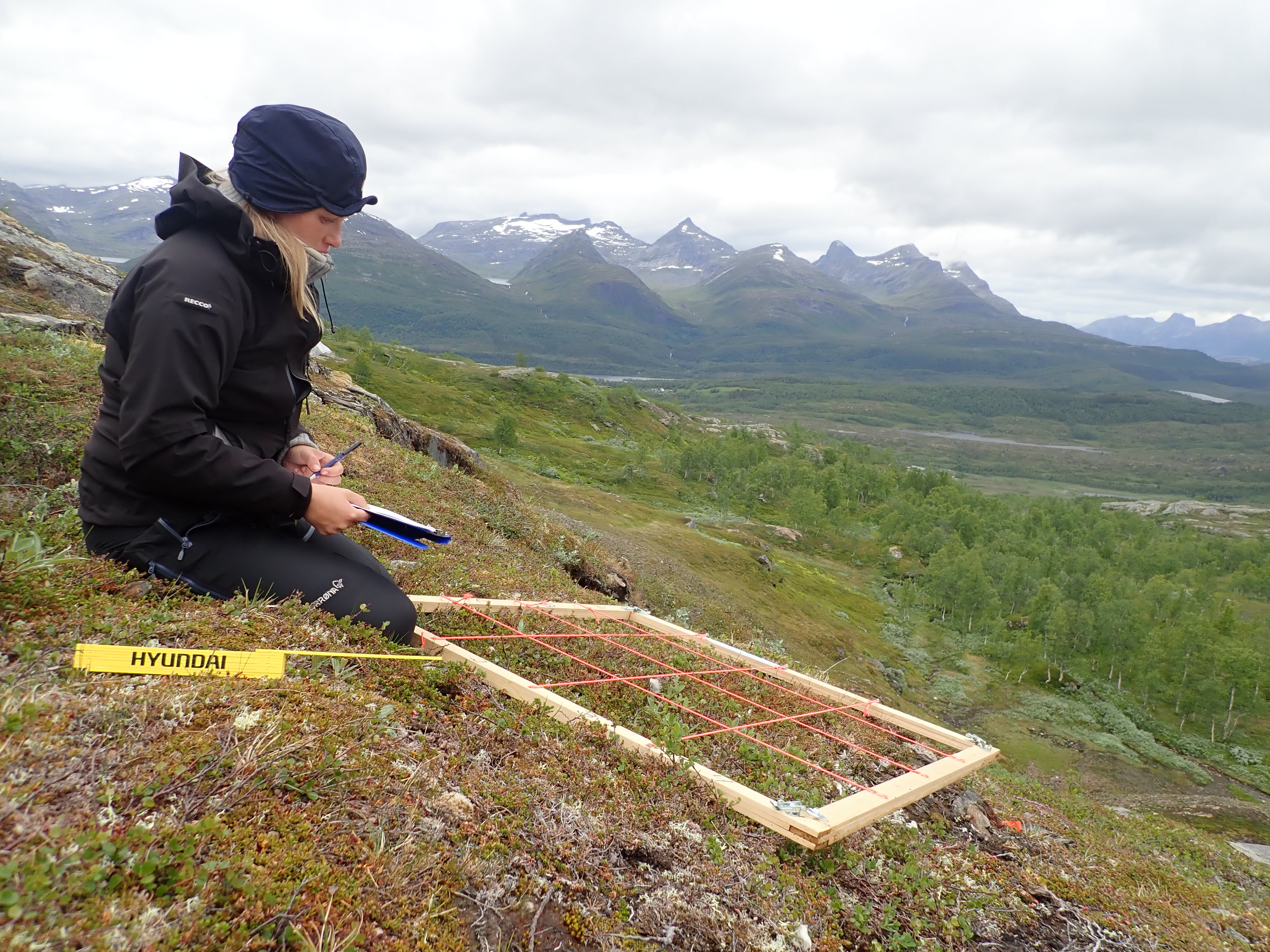
The transect: This dataset consists of a corridor sampled using aiborne laser scanners (200 m wide and 1,500 km long). The transect stretches from south to north in Norway and passes many transition zones between forest and alpine areas. Field measurements of trees and surrounding vegetation, have been carried out on 36 field sites along the transect. Laser scanner data have been collected over the transect in 2006/2007 and 2012/2013. Field work efforts were carried out in 2008, 2012 og 2018. A drone was used to collect remotely sensed data for the field sites in 2018 . Together with climate data and data describing herbivore pressure, the dataset is going to be used for analyses that aim at disentangling the effects of climate and changed land use on the changes in the tree line ecotone.
Hol/Setesdal: This dataset comprise controlled experiments where the vegetation partly have been protected from herbivores, and partly not. The dataset will be used to analyze how different levels of hebivore pressure affect the etablishment of trees in the tree line ecotone.
Production forest: This dataset comprise data from several operational forest inventories in the south-eastern part of Norway. For all the different locations, inventories at two different points in time are available. This enables analyses related to potential increased growth in the lowland forest as a result of a changing cllimate.
News:
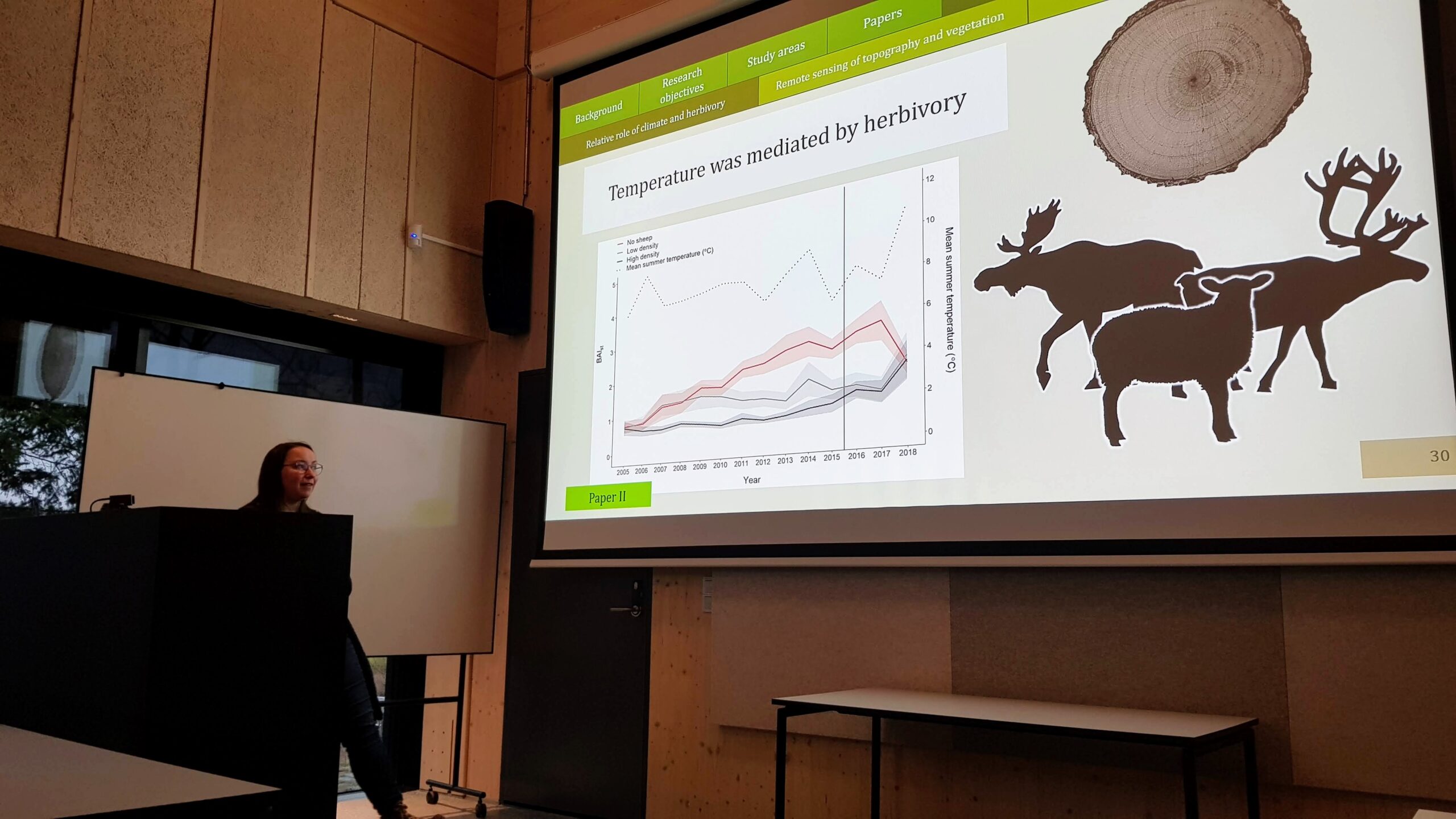
2022.11.24: Sluttseminar
2020.11.12: Field work – Soil Carbon
2020.03.10: Project meeting
2018.10.12: Field work in the transect complete.
2018.03.23: Successfull startup meeting.
Coordninator
Norwegian University of Life Sciences, Norway
Dr. Ole Martin Bollandsås
Email: olebo[at]nmbu.no
Prof. Erik Næsset, Prof. Terje Gobakken, Prof. Hans Fredrik Hoen, Prof. Kari Klanderud
Project partners
Center for International Climate and Environmental Research (CICERO)
Hans Asbjørn Aaheim
Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU)
Prof. Gunnar Austrheim
Scientific collaborators
University of British Columbia, Canada (UBC)
Prof. Nicholas C Coops
University of Idaho, USA (UoI)
Dr. Jan Eitel
Finnish Meteorological Institute, Finland (FMI)
Prof. Jari Liski
Private sector collaborators
Viken Skog SA
Head of Dept. Svein Dypsund
Mjøsen Skog SA
Head of Dept. Geir Korsvold
Time period
2018 – 2021
Funding
Norwegian Research Council (NFR)
Norwegian University of Life Sciences (NMBU)
Related posts